Electric generator is a simple device, that produces electricity from other kinds energy. Most of the industrial ones use heat from burning coal or even an atomic energy, but simplest of them use mechanical energy. Building one of such models isn’t very hard task, you won’t need any special materials or precise skills. Of course, such device won’t be enough to power your home, but it presents a fun challenge to your engineering skills. Get all the materials you need on Jiji.
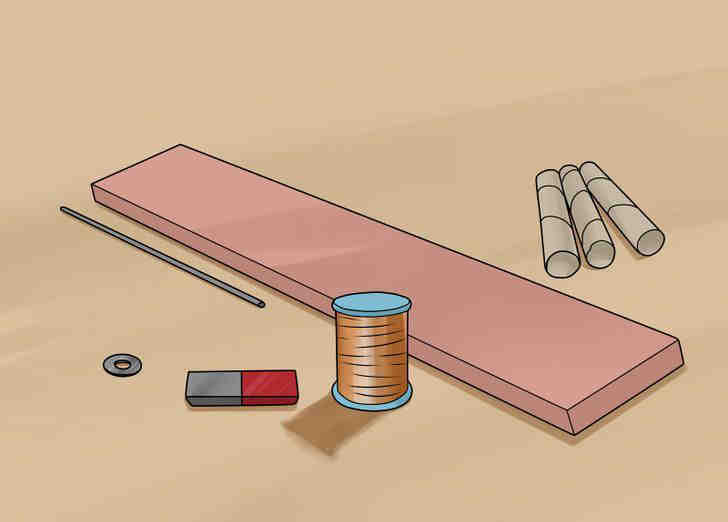
- The materials you need are (calculations were made for the simplest example):
- 0.5 mm thick enameled copper wire. The more windings of the coil you’ll make with it, the more the power output will be.
- 10 cm bar magnet
- Large paper or cardboard tube, magnet should fit in it with a little clearance
- 0.5 cm in diameter steel or aluminum rod, 30 cm in length
- Lumber for a frame of the generator
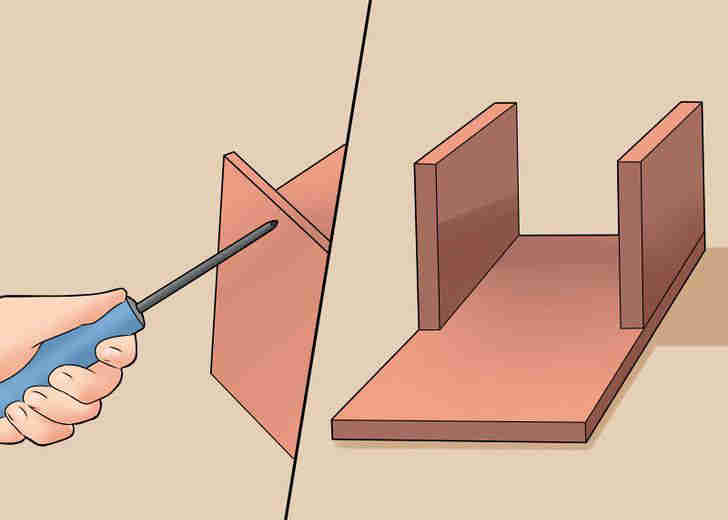
- Build a U-shaped frame for your generator. Nail or screw two pieces of lumber perpendicular to the third, base one.
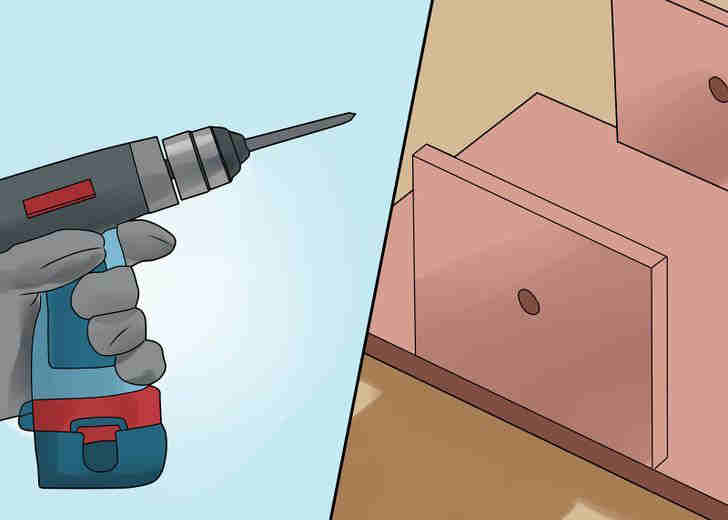
- Drill a hole in each side pieces of lumber, one in front of the other. The diameter of each hole should be corresponding to the diameter of the steel or aluminum rod. Get yourself the best instruments on Jiji.
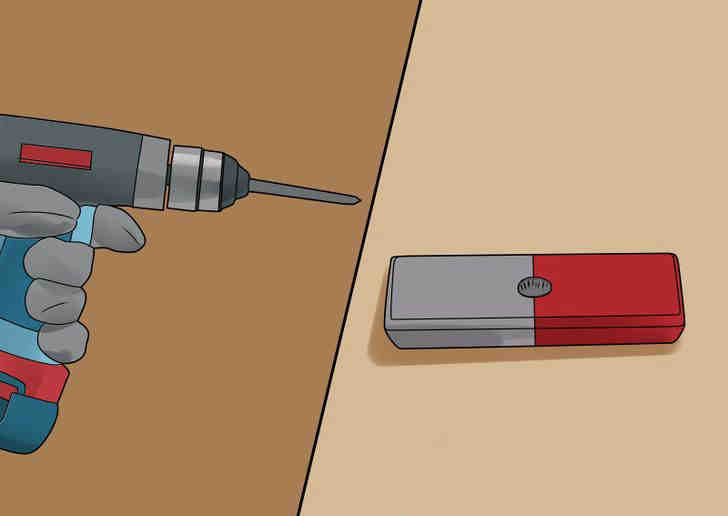
- Drill the same hole in your magnet. Be careful, as they are usually crumbly.
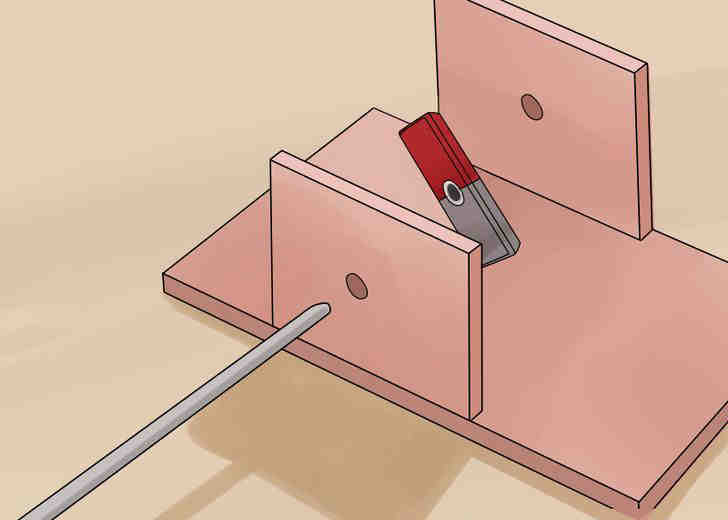
- Slide the metal shaft through the holes in the frame and the magnet. Make sure, that the magnet is perpendicular to the shaft.
- To keep the magnet still in relation to the shaft, glue it with a high-strength hot melt glue or epoxy.
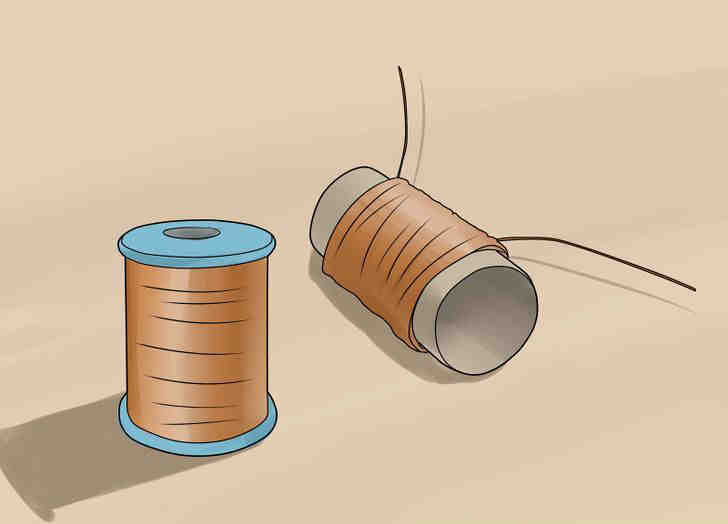
- Wind the copper wire around your cardboard or paper tube. Leave about 40 cm of wire loose on each end in order to connect it to the test subject (light bulb or LED). This is where the current in your generator will flow.
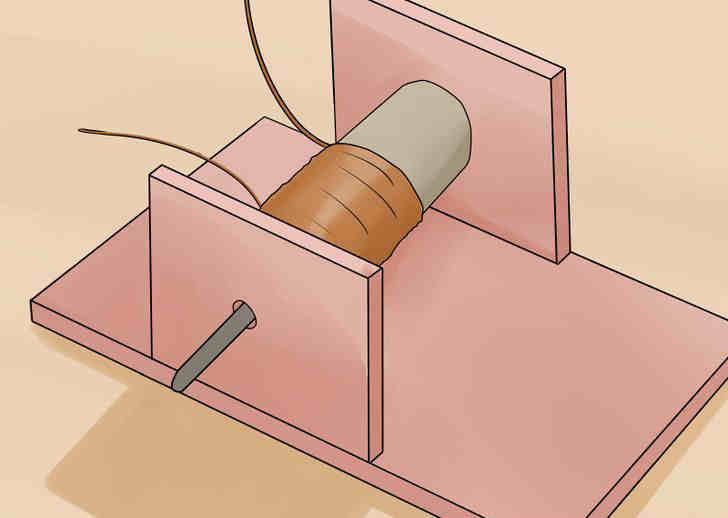
- Slide the tube over the magnet. Make sure, that the rod with the magnet turns freely in the tube. For a better stability, use some kind of stiff wire frame to support the tube near its center
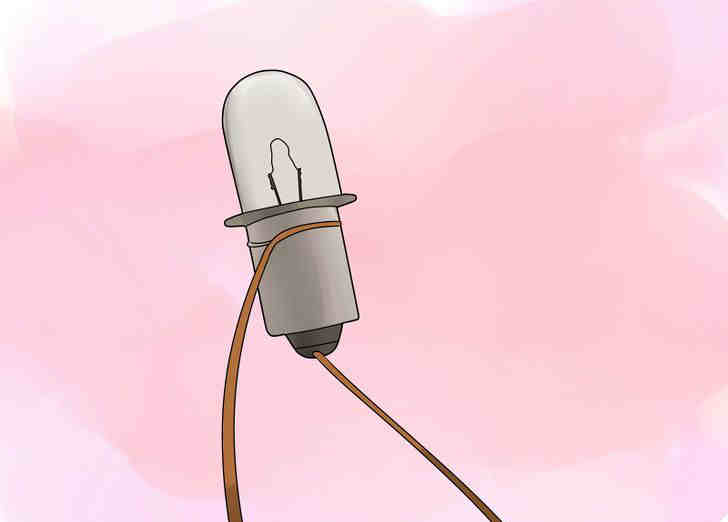
- Attach two wires you have on the ends of a tube to the light bulb, LED or simply a multimeter.
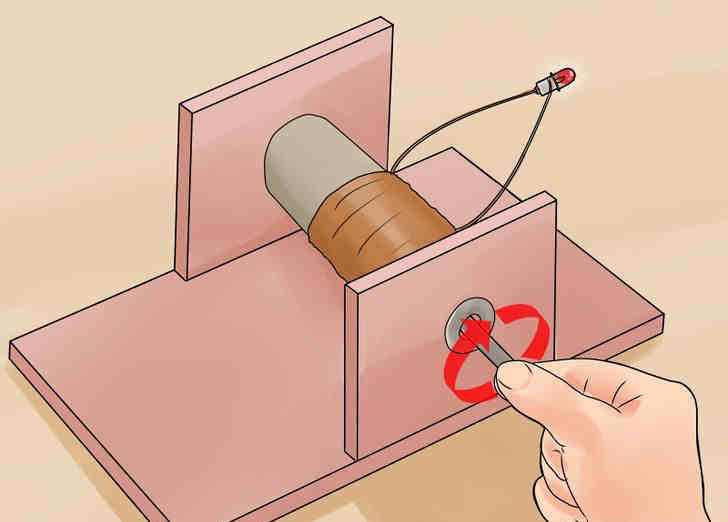
- Spin the rod as fast as you can. Changing magnetic field of the rotating magnet will cause an inductive current in your copper coil. You’ll get a small voltage, which should be enough for a lightbulb. You can use a motor to increase the number of spins of the magnet, therefore increasing the value of the current.










